Wave Intensity wall analysis
Wave intensity analysis was introduced as an alternative method in the study of cardiovascular dynamics and arterial-ventricular interaction. Originally, the concept demanded invasive measurement of blood pressure and velocity but further development resulted in an ultrasound based non-invasive wave intensity system (the Aloka system). The aim of this project is to develop and test a new approach for wave intensity measurements based on speckle-tracking data acquired in the vascular wall, having the advantages of being less time-consuming, non-invasive and applicable in vessels with low flow.
Methods
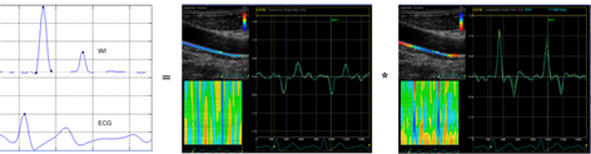
Within wave intensity analysis, arterial waves are defined as sequential infinitesimal changes of blood pressure and velocity. Our new method, wave intensity wall analysis (WIWA), approximates these changes by measurements of strain rate in the radial and the longitudinal direction; the pressure component (dP/dt) is approximated by strain rate in the radial direction and the blood velocity changes (dU/dt) by strain rate in the longitudinal direction. Positive strain corresponds to stretching and negative strain to compression relative to the original length. Thus, the radial component is sign-reversed in the WIWA calculations.
Results
The WIWA method has been validated against a commercially available wave intensity system, the Aloka system, showing good results. The method has further been applied in patients with end stage renal disease to study the effects of a single session of hemodialysis on cardiovascular function. This study showed that wave intensity indexes adjusted for differences in preload may contribute in the assessment of true LV contractility and relaxation. Future aims are to further investigate the feasibility of the method in the assessment of the cardiac contractility, and to expand the method to include data enabling the assessment of local arterial stiffness.
Collaborations
This is a collaboration project between STH (School of Technology and Health, KTH), the Department of Clinical Physiology, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm and Evangelical Medical School, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil.
Contact persons
and
Search words
Ultrasound, speckle tracking, wave intensity, contractility, arterial-ventricular interaction
