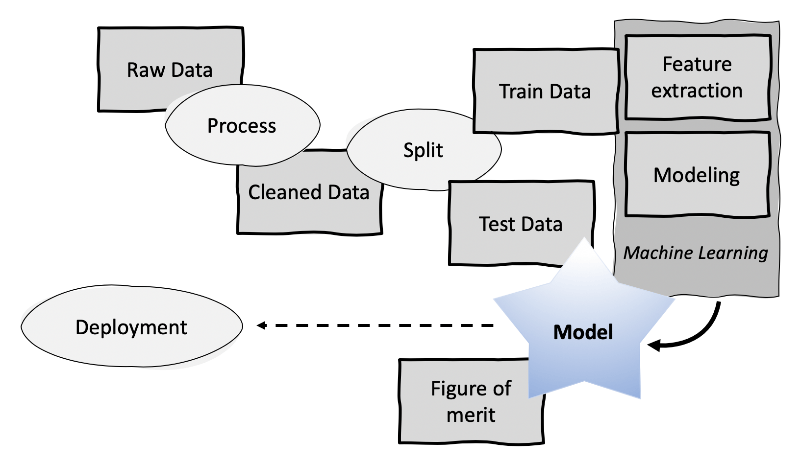
Course starts with an overview of what machine learning is and why it is important. This is illustrated with several real applications in various media, e g text summarisation, sound and music recommendation and image retrieval. The course then presents the workflow of machine learning development that serves as an overview of the remainder of the course. The course presents the two general classes of machine learning methods: supervised learning (for example closest neighbour, decision tree) and unsupervised learning (e g k-means clustering, principal component analysis). For these, the course presents different types of modelling: parametric (e.g. Bayes, least squares) and non-parametric (for example closest neighbours, decision trees). The course reviews common methods for evaluation of machine learning models (e g holdout, bootstrap). Finally, best practices are presented (e.g. partition) together with common pitfalls (e g over fitting).
DM1590 Machine Learning for Media Technology 7.5 credits
Information per course offering
Choose semester and course offering to see current information and more about the course, such as course syllabus, study period, and application information.
Information for Spring 2026 Start 16 Mar 2026 programme students
- Course location
KTH Campus
- Duration
- 16 Mar 2026 - 1 Jun 2026
- Periods
Spring 2026: P4 (7.5 hp)
- Pace of study
50%
- Application code
60850
- Form of study
Normal Daytime
- Language of instruction
English
- Course memo
- Course memo is not published
- Number of places
Places are not limited
- Target group
- Open for CMETE
- Planned modular schedule
- [object Object]
- Schedule
- Part of programme
Contact
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus DM1590 (Spring 2025–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
After passing the course, the students should be able to:
- develop and modify media technology applicationsthat use machine learning and evaluate them in an appropriate manner,
- recommend methods for machine learning for particular media technology applications,
- describe and explain the machine learning pipeline,
- explain and contrast supervised and unsupervised learning methods,
- explain and contrast parametric and non-parametric methods,
- explain training validation and testing of machine learning models,
- summarise best practice and pitfalls in applied machine learning for media technology
in order to
- being able to apply and evaluate machine learning models and methods in media technology.
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
Knowledge and skills in programming, 6 higher education credits, equivalent to completed course DD1310-DD1318/DD100N/DD1331/DD1337/ID1018.
Knowledge in probability theory and statistics, equivalent to completed course SF1919.
Active participation in a course offering where the final examination is not yet reported in LADOK is considered equivalent to completion of the course.
Registering for a course is counted as active participation.
The term 'final examination' encompasses both the regular examination and the first re-examination.
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- LABA - Laboratory work, 3.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- ÖVNQ - Exercises, 1.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
- PROA - Project, 3.0 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.
Further information
Course room in Canvas
Offered by
Main field of study
Education cycle
Supplementary information
In this course, the EECS code of honor applies, see:
http://www.kth.se/en/eecs/utbildning/hederskodex