Electrostatics: Field and potential, Gauss’s theorem, metals and dielectrics, the capacitor, electrostatic energy.
Magnetism: Sources of the field, force and torque, magnetic materials and magnetic energy, technical applications, induction and inductance, mechanical waves.
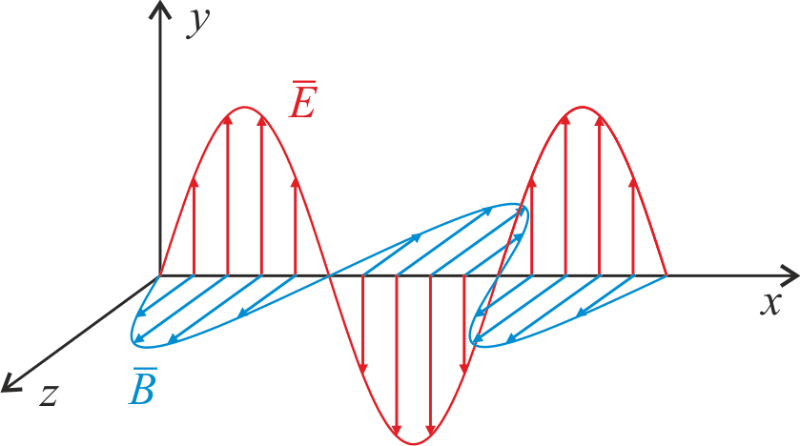
Electromagnetic waves: Geometrical optics, polarization, interference and diffraction, coherence.
After the course, the student will be able to:
- solve technical problems, relevant for the program, which are related to electrical fields, magnetic fields, mechanical waves, and electromagnetic waves
- explain physical problems, conditions and restrictions to cooperation partners with non technical educations
- estimate size and reasonableness in physical problems
- use and understand restrictions in physical measurements and instruments
- evaluate and present physical measurements in text and in diagrams.
“Physical” in the text above, means that part of physics that is included in the syllabus (se below).