The course provides the foundation of cardiovascular biomechanics from the organ to the tissue level. A quantitative approach to human physiology from the biomedical engineering perspective is presented, where structural and hemodynamic aspects are addressed. In-vitro experimental and analytic tools are developed and used to solve problems in cardiovascular biomedical engineering. Techniques include Finite Element (FE) modeling, model parameter identification, non-linear continuum mechanics, constitutive descriptions of passive and active properties of blood vessels, Newtonian and non-Newtonian descriptions of blood.
SE2121 Introduction to Biomechanics 9.0 credits
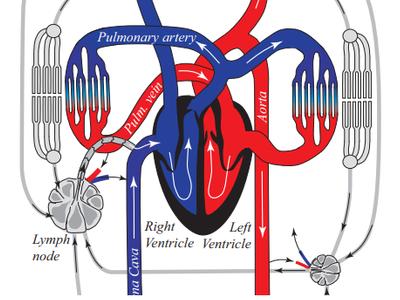
Please watch the Introduction video
The course provides the foundation of cardiovascular biomechanics.In vitro experimental tools are linked to analytical methods, to solve problems in cardiovascular biomedical engineering. Techniques include Finite Element (FE) modeling, system analysis, model parameter identification, linear and non-linear continuum mechanics, constitutive descriptions of the passive properties of blood vessels, Newtonian and non-Newtonian descriptions of blood.
Information per course offering
Choose semester and course offering to see current information and more about the course, such as course syllabus, study period, and application information.
Information for Spring 2026 Start 16 Mar 2026 programme students
- Course location
KTH Campus
- Duration
- 16 Mar 2026 - 1 Jun 2026
- Periods
Spring 2026: P4 (9 hp)
- Pace of study
50%
- Application code
60652
- Form of study
Normal Daytime
- Language of instruction
English
- Course memo
- Course memo is not published
- Number of places
Min: 10
- Target group
- No information inserted
- Planned modular schedule
- No information inserted
- Schedule
- Schedule is not published
Contact
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus SE2121 (Spring 2022–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
Biomechanics applies engineering/mechanical principles and methods to biological systems and aims at understanding their normal (physiological) and abnormal (pathological) responses. Biomechanics is a rapidly growing field of engineering and plays a dominant role in the development of medical devices, for example. The course provides the foundation of cardiovascular biomechanics from the organ to the tissue level. Specifically, a quantitative approach to human physiology from the biomedical engineering perspective is presented, where both structural and hemodynamic aspects are addressed. In-vitro experimental and analytic tools are developed and used to solve problems in cardiovascular biomedical engineering.
After the course, the participants should be able to
- Understand the basics of vascular physiology
- Model a particular bioengineering problems by selecting appropriate modeling assumptions
- Understand the purpose, function, implication and limitation of biomechanical modeling
- Achieve a theoretical understanding of non-linear continuum mechanics
- Solve a particular problem by using either analytical approaches or the FE method
- Combine and integrate different solution strategies to address more challenging problems
- Achieve a practical understanding in applying the FE method as demonstrated by solving typical problems of bioengineering interest
- Present, analyze and explain derived results in a clear and causal way
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
English B / English 6
Basic course in solid mechanics (for instance SE1010, SE1020 or SE1055) and a Finite Element (FE) course (for instance SE1025).
Recommended prerequisites
SE1010, SE1020, SE1021 or SE1055 Solid mechanics basic course and
SE1025 FEM for engineering applications or equivalent
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- HEMA - Home Assignment, 3.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
- TENA - Examination, 4.0 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
- LABA - Laboratory Work, 2.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Other requirements for final grade
Laboratory work (LAB1, 2.0 credits), Home assignments (HEM1, 3.0 credits) and Examination (TEN1, 4.0 credits)
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.