The course focuses on wireless networks and machine-learning methods for wireless Internet of Things (IoT). The course starts with an introduction of applications of wireless IoT. Thereafter, methods for wireless communications protocols with an emphasis on analytical performance analysis are treated. In the course, machine-learning algorithms that can be executed on wireless IoT systems are analysed, where data and computations are distributed. The interplay between wireless network and machine-learning is analysed based on theoretical methods.
EP2700 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks 7.5 credits
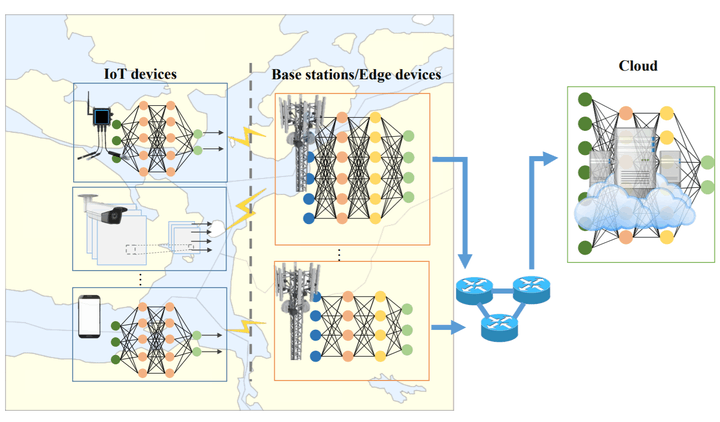
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) the essential infrastructure of the Internet of Things. WSNs are networks of wireless nodes equipped with sensing capabilities for a huge variety of applications, such as body monitoring, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, industrial automation, or smart grids. The focus of the course is on communication and data analysis protocols and algorithms for networking, signal processing and machine learning in WSNs. The course presents the essential design and perofrmance analysis methods for networking and machine learning by WSNs.
Information per course offering
Information for Autumn 2025 Start 25 Aug 2025 programme students
- Course location
KTH Campus
- Duration
- 25 Aug 2025 - 24 Oct 2025
- Periods
Autumn 2025: P1 (7.5 hp)
- Pace of study
50%
- Application code
51301
- Form of study
Normal Daytime
- Language of instruction
English
- Course memo
- Course memo is not published
- Number of places
Places are not limited
- Target group
- Open for all programmes as long as it can be included in your programme.
- Planned modular schedule
- P1: B1, F1, F2, G2.
- Schedule
Contact
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus EP2700 (Autumn 2023–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
After passing the course, the student should be able to
- give an account of the central wireless network protocols for IoT system design
- give an account of central machine-learning methods for wireless IoT systems
- design machine-learning methods for wireless IoT systems
- theoretically characterise performance for wireless communications protocols and machine-learning methods with distributed datasets
in order to
- understand and explain which design options there are for a specific wireless communication system
- understand and explain which design alternative is available for a specific machine-learning algorithm with distributed datasets
- be able to give arguments for which type of performance should be prioritised for designing wireless IoT systems and machine-learning methods
- understand and explain design alternative for machine learning for specific datasets distributed over a wireless IoT system.
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
- Knowledge in one variable calculus, 6 higher education credits, equivalent to completed course SF1625/SF1673/SF1685.
- Knowledge in computer communication, 6 higher education credits, equivalent to completed course IK1203/EP1100.
- Knowledge in probability theory, 6 higher education credits, equivalent to completed course SF1900-SF1935.
- Knowledge in signals and systems, 6 higher education credits, equivalent to completed course EQ1110/EQ1120.
- The upper secondary course English B/6.
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- INL1 - Assignment, 1.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
- INL2 - Assignment, 1.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
- TEN1 - Examination, 4.5 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
- INL3 - Assignment, 1.0 credits, grading scale: P, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.
Further information
Course room in Canvas
Offered by
Main field of study
Education cycle
Supplementary information
In this course, the EECS code of honor applies, see:
http://www.kth.se/en/eecs/utbildning/hederskodex.