Two- and three-dimensional sound reproduction, surround formats. A/D and D/A conversion for audio in detail. Studio signal processing. Data reduction methods. Integrated circuits for audio. Hard disks and audio. Optical disks in audio. Sound quality assessment. Software architectures for audio. Audio in broadcasting. The course assignment involves writing an in-depth article on a self-selected sub-topic in audio. Several guest lecturers contribute with their expertise. For a detailed description, please see the home page of this course.
DT2410 Audio Technology 7.5 credits
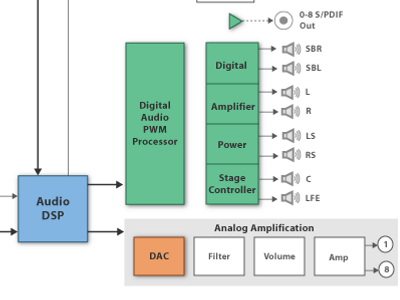
This course presents the principles and current techniques for the production, processing and distribution of sound, especially music and speech. The course gives an integrated overview of how modern audio systems are constructed and used, with analogue and digital audio techniques, in combination with general storage and communication technology.
Information per course offering
Course offerings are missing for current or upcoming semesters.
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus DT2410 (Autumn 2021–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
The participants shall upon completion of this course
- be able to specify at a block diagram level the functions/components that must or may be included in audio systems for various applications; with regard for technical constraints such as channel count, converter types, data reduction methods, power requirements and storage
- be able to assess audio systems with regard to sound quality and suitability in given applications
- be acquainted with how real-time audio data are usually managed in audio software and in operating systems
- have obtained basic experience with using a mixing desk and its major peripherals such as dynamics processor, reverb unit and equaliser
- be able to understand the first few pages of data sheets for audio integrated circuits
- be able to participate in the planning, deployment and maintenance of new and existing systems
- have a broad perspective on how transforms, signal theory, discrete mathematics, information theory, electronics and physics all come together in audio applications
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
Single course students: 90 university credits including 45 university credits in Mathematics or Information Technology. English B, or equivalent.
Recommended prerequisites
The prerequisite knowledge varies with the background of the participant. This course is elective for Media 4-5, E4 and D4. In the Media Technology programme, the course is taken as part of a major (with thesis) or a minor (without thesis) in Sound.
For Media 4-5: DT1175 Sound and DM1135 Multimedia systems and signals.
All others: some fundamentals of electrical engineering with signal theory and signal processing, and some acoustics. If in doubt, please e-mail the examiner with your course record.
Media Technology: the theory for perception of sound and for what is communicated to the listener. Electrical Engineering: the theory of audio signals and digital technology in audio systems. Computer Science: the theory for sound-based man-machine interaction, and systems programming.
Equipment
Literature
Examination and completion
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Grading scale
Examination
- ANN1 - Assignment, 1.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- LAB1 - Laboratory Course, 1.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- TEN1 - Examination, 4.5 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
Opportunity to complete the requirements via supplementary examination
Opportunity to raise an approved grade via renewed examination
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.
Further information
Course room in Canvas
Offered by
Main field of study
Education cycle
Add-on studies
Please discuss with the instructor.
Contact
Supplementary information
In this course, the EECS code of honor applies, see:
http://www.kth.se/en/eecs/utbildning/hederskodex