Andreas Archenti
Professor
Details
Researcher
About me
Professor Andreas Archenti is actively engaged in precision-driven research within the area of machinery reliability and performance. Since 2018, he has held the position of Chair Professor in Industrial Dependability with a particular emphasis on Precision Engineering, Metrology, and Analytics at KTH Royal Institute of Technology. He earned his M.S. in Mechanical Engineering with a focus on Mechatronics in 2007 and completed his PhD in Machine and Process Technology in 2011. In 2014, he was appointed as a docent in Precision Manufacturing and Metrology at KTH.
As the Director of the Center for Design and Management of Manufacturing Systems (DMMS) at KTH, Dr. Archenti is responsible for coordinating activities related to research, education, and the dissemination of information between academia and the manufacturing industry.
Education
- 2011 - Phd in Machine and Process Technology
- 2007 - MSc (Civilingenjör) in Mechanical engineering focusing on Mechatronics
Research interesst
Precision engineering is a strategic process that leverages advanced knowledge, cutting-edge technologies, and innovative methods to develop novel or substantially improved products, systems and services.
Precision manufacturing and integrated metrology involve producing and characterizing a product's dimensions, geometry, and surface properties, as well as measuring, monitoring, and controlling equipment reliability and performance. Today, research in precision-driven manufacturing and metrology spans a wide spectrum, from large components in the aerospace, automotive, and energy industries to micro/nano fabrication for semiconductor or medical industries. Moreover, precision engineering plays a vital role in ensuring the quality of various products, including wafers in lithography, medical devices, and optical equipment. We can see examples of precision manufacturing and metrology in large-scale science projects, such as the alignment of cryomagnets at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN and the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) for gravitational research, or the James Webb whose 132 actuators position the mirrors with 10 nanometer accuracy. But we can also perceive its impact on daily goods, for example in the fabrication of moulds for contact lenses and its posterior measurement and quality assurance.
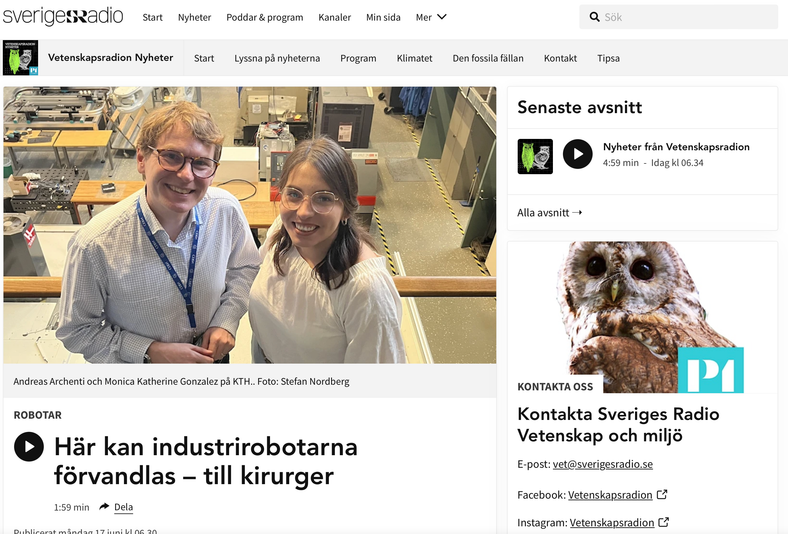
He is currently involved in a research collaboration with the University of Tokyo on robotics for scientific exploration applied to biomedical applications. You can hear more about it in this clip from Swedish Science Radio.
Courses
Advanced Manufacturing Equipment (MG2047), examiner, course responsible
Advanced Manufacturing Technology (MG2009), teacher
Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Extended Course (MG2109), teacher
Advanced Metrology (MG2110), examiner
Decision-making for Advanced Manufacturing (MG2045), examiner
Degree Project in Production Engineering and Management, Second Cycle (MG213X), examiner
Degree Project in Production Engineering, Second Cycle (MG212X), examiner
Degree Project in Sustainable Production Development, Second Cycle (ML230X), examiner
Degree Project in Sustainable Production Development, second cycle (ML231X), examiner
Industrial Analytics for Advanced Manufacturing (ML2306), course responsible, examiner
Modern Industrial Metrology (MG2010), teacher, examiner
Scientific Methodology for Production Engineering (MG2100), teacher