Human Body Model with Active Muscles and Detailed Brain for Pedestrian Protection Research
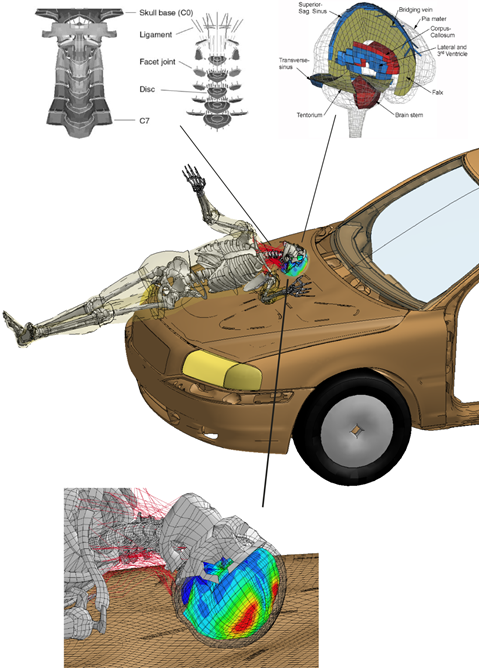
Pedestrian accidents comprise a significant part of the fatalities found in traffic accidents, making it a prioritized research field both in Sweden and internationally. The head is one of the most vulnerable body parts in the body why this project focus on improving the predictability of head and brain injury in a state-of-the-art human body FE model. One emphasis in this project is on pre-crash activated neck muscles and its effect on head-to-vehicle interaction. The model is also used in accident reconstructions by correlating injuries and damages from real life accidents in order to gain better understanding of injury mechanisms. The aim is that the gained knowledge will help in understanding how injuries can be reduced and provide the vehicle industry with better tools in their work in improving pedestrian protective systems.
Publications
Alvarez, V.S, Halldin, P, Kleiven, S, The Influence of Neck Muscle Tonus and Posture on Brain Tissue Strain in Pedestrian Head Impacts, (2014), Stapp Car Crash Journal, Vol. 58
Alvarez, V.S, Halldin, P, Kleiven, S, Influence of Neck Muscle Tone on Brain Tissue Strain during Pedestrian Impacts, (2014) 11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI), 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V), July 20 - 25, 2014, Barcelona, Spain
Alvarez AS, Fahlstedt M, Halldin P, Kleiven S. Importance of Neck Muscle Tonus in Head Kinematics during Pedestrian Accidents. (2013) Proc. IRCOBI Conf. on the Biomechanics of Impacts, pp 747-761
Fahlstedt, M, Halldin, P, Kleiven, S, Comparison of multibody and finte element human body models in pedestrian accidents with the focus on head kinematics, Traffic Injury Prevention, Vol 17, Nr 3
Collaboration
Autoliv Development
Volvo Car Corporation

