The course objective is to provide a strong introduction to organic chemistry in terms of structure and reactivity, practical synthetic work and green chemistry. The course also provides a solid base for further specialization in organic chemistry.
Short course description:
- Nomenclature
- Conformation/configuration
- Reaction mechanisms
- Frontier molecular orbital theory
- Proton transfer/pKa
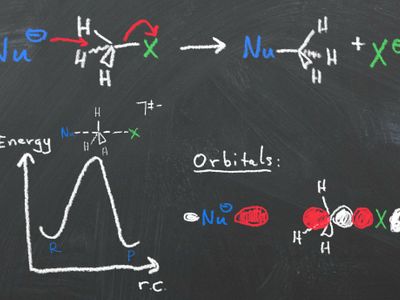
- Substitution/elimination
- Addition reactions
- Green chemistry
Detailed course description:
- applying the organic chemistry language, e.g. describe organic structures graphically, naming organic compounds according to the IUPAC nomenclature, give trivial names for some common compounds and describe the three- dimensional structure of organic compounds graphically and according to CIP nomenclature.
- identifying and ranking nucleophiles, electrophiles, acids and bases in a chemical reaction.
- how acid/base equilibrium/pK /proton transfer influence the outcome of a reaction.
- electron (arrow) pushing to describe reaction mechanisms.
- frontier molecular orbital theory to categorize which orbitals that are HOMO and LUMO in organic molecules and apply these to determine the outcome of a reaction.
- based on reaction conditions predict if a reaction proceeds through a SN1, SN2, E1 or E2 mechanism and explain the stereochemical and regiochemical outcome. Inversely, describe reaction conditions to control a reaction so that it proceeds via a SN1, SN2, E1 or E2 mechanism.
- an organic compound’s stereochemistry to determine its conformation and reactivity.
- the reaction mechanism and the stereo- and regiochemical outcome of additions of electrophiles to alkenes.
- the concept of green chemistry and its application in organic chemistry and how this can apply for sustainable development.
- basic spectroscopic methods (NMR) for structural analysis of organic compounds.
- risk analysis and safety assessment of an organic chemical reaction process and understand the safety precautions required for laboratory work.
- turning a recipe into a complete synthesis, which includes setting up the reaction, do work up and purification of the desired compound by means of extraction, distillation and crystallization.
- structure determination of organic compounds using the most common analytical methods (melting point, NMR, IR)
- basic synthesis planning, which includes extracting relevant information from organic chemistry databases, design and execute an organic reaction process and report the result.