How it works?
The main objective of ISAAC is to develop, build and demonstrate a system with two Free-Falling Units (FFUs), where, after being ejected from a sounding rocket, one FFU is able to optically track the other, i.e. to keep the other FFU within a narrow field of view. The secondary objective is to determine the CO2 concentration profile in the middle atmosphere by means of IR spectroscopy - an example of an application of the above-mentioned tracking. The two FFUs named ISAAC-Tx and ISAAC-Rx will be located inside a rocket mounted unit (RMU), which in turn will be placed inside the REXUS vehicle, a REXUS sounding rocket. The FFUs have a common and a specific unit. The common unit is identical for both FFUs.
Once ejected from the rocket, the experiment is completely autonomous. It is equipped with a parachute, a GPS system, a satellite modem and a radio beacon, allowing it to land softly and transmit its location, thus making a recovery possible. Post-flight analysis will allow reconstructing the trajectory of the FFUs, assessing the tracking performance and evaluating the results from the spectroscopy.
The Rocket Mounted Unit
The rocket cylinder is a modified 300mm REXUS rocket module. Two openings, 254mm wide and 85mm high, have been cut for the FFU ejection. Since these two openings weaken the module, the thickness has been increased from 4mm to 8mm near the openings to match the strength tolerance of a basic REXUS module.
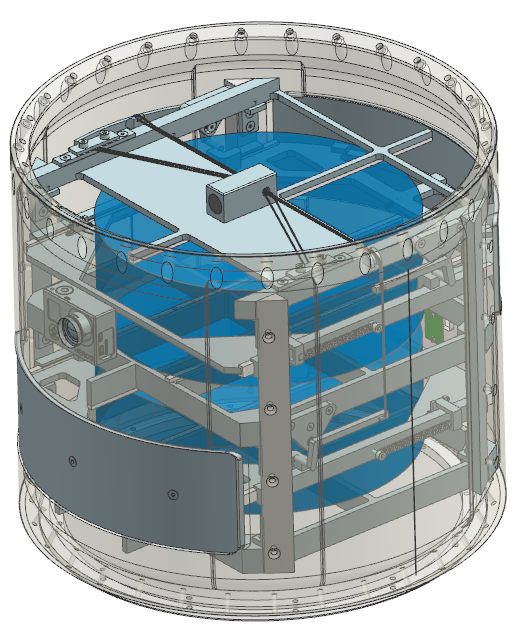
The ejection is triggered by a pyro cutter. Before ejection, the FFUs (blue cylinders) are retained by two self-disengaging hooks on each side. Ejection springs provide a sufficient ejection speed to the FFUs.
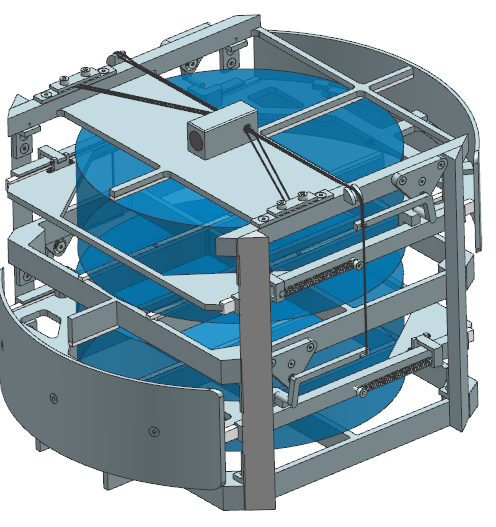
The Common Unit
The components inside the CU are: battery, GPS antenna, STX antenna and the PCB. These are screwed onto the bottom plate. The parachute is placed on top of the components.

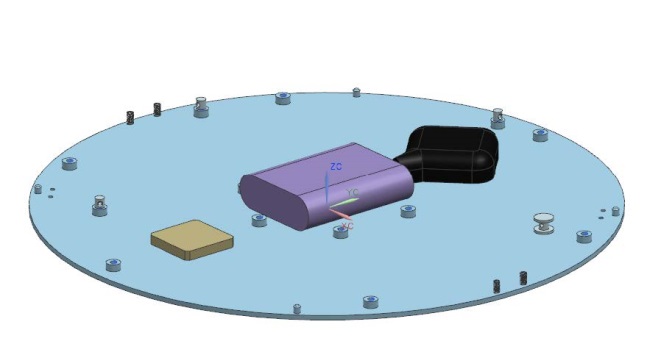
For recovering purposes the FFUs are equipped with a parachute system and will start transmitting their position, once the parachutes are deployed, both through a satellite modem and a radio beacon transmitter. Also, in order to make sure that the FFUs can withstand the environment in which they will land tests will be performed for different landing scenarios, for example a prolonged exposure to humidity and cold.
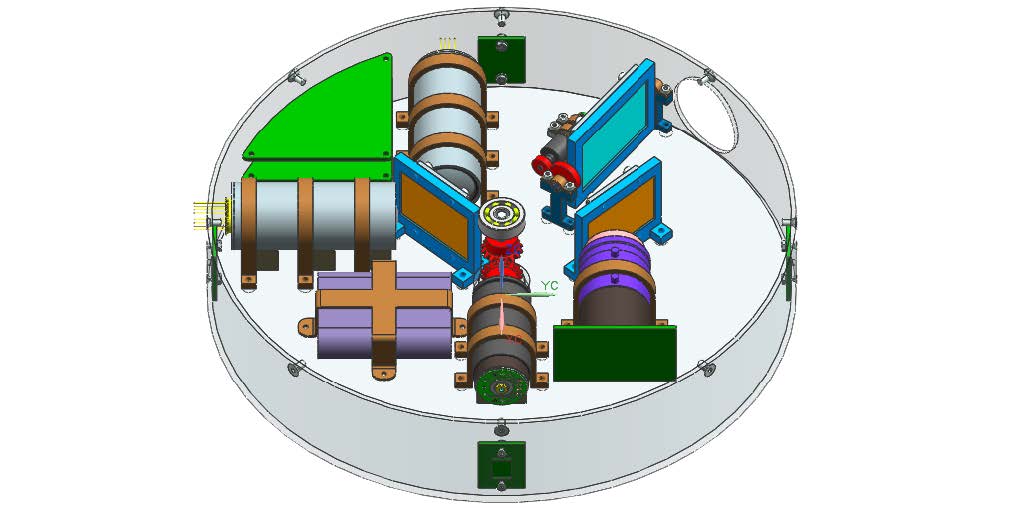
The ISAAC-Tx
The main purpose of this unit is to emit the light sources for both tracking (20 red LEDs) and IR spectroscopy (6 thermal sources).
The ISAAC-Tx is entirely passive in the tracking process.
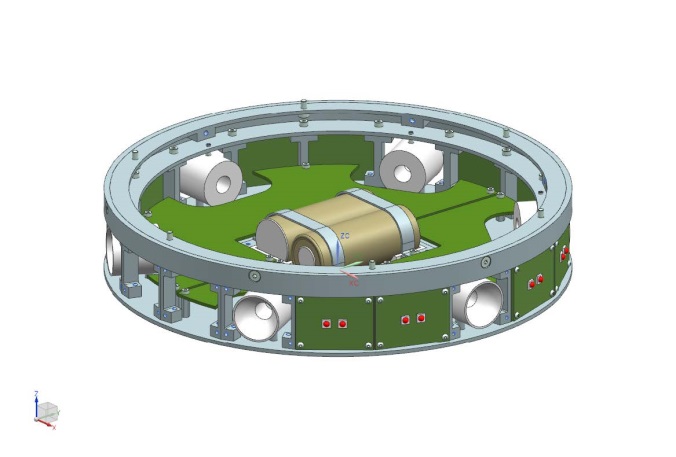
The ISAAC-Rx
The ISAAC-Rx has a tracking camera, controlled via a stepper motor, to find the light emitted from ISAAC-Tx and the sensors required for the spectroscopy. It has a non-spinning part, the specific unit, which will be pointed towards ISAAC-Tx with a two-degree-of-freedom control.
Once the tracking is initiated the scientific part of the experiment takes place.