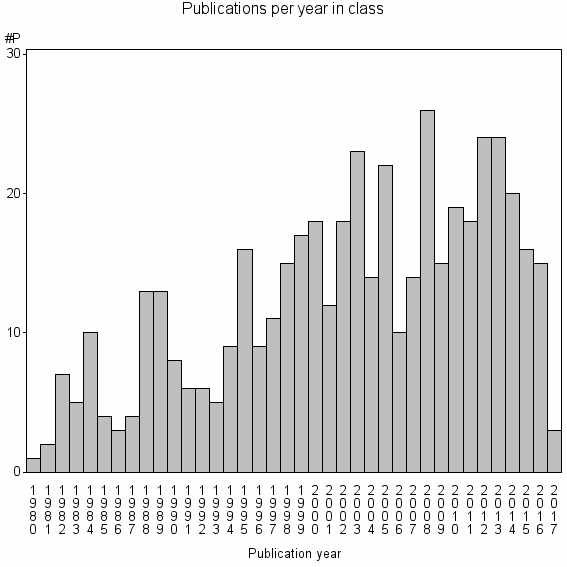
Class information for: |
Basic class information |
| Class id | #P | Avg. number of references |
Database coverage of references |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20128 | 475 | 19.9 | 25% |
Hierarchy of classes |
The table includes all classes above and classes immediately below the current class. |
| Cluster id | Level | Cluster label | #P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | ECONOMICS//EDUCATION & EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH//PSYCHOL | 3876184 |
| 175 | 3 | PHILOSOPHY//PHILOSOPHICAL STUDIES//SYNTHESE | 58071 |
| 1117 | 2 | PHILOSOPHY//ANALYSIS//JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHICAL LOGIC | 9695 |
| 20128 | 1 | VAGUENESS//EPISTEMICISM//SORITES PARADOX | 475 |
Terms with highest relevance score |
| rank | Term | termType | Chi square | Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
#P with term in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VAGUENESS | authKW | 709403 | 11% | 21% | 52 |
| 2 | EPISTEMICISM | authKW | 393737 | 1% | 88% | 7 |
| 3 | SORITES PARADOX | authKW | 353551 | 2% | 50% | 11 |
| 4 | COXS THEOREM | authKW | 257136 | 1% | 100% | 4 |
| 5 | HIGHER ORDER VAGUENESS | authKW | 231417 | 1% | 60% | 6 |
| 6 | SORITES | authKW | 196862 | 1% | 44% | 7 |
| 7 | BORDERLINE CASES | authKW | 185281 | 1% | 41% | 7 |
| 8 | PHILOSOPHY | WoSSC | 148651 | 88% | 1% | 416 |
| 9 | MARGIN FOR ERROR | authKW | 144637 | 1% | 75% | 3 |
| 10 | ONTIC VAGUENESS | authKW | 144637 | 1% | 75% | 3 |
Web of Science journal categories |
| Rank | Term | Chi square | Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
#P with term in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Philosophy | 148651 | 88% | 1% | 416 |
| 2 | History & Philosophy of Science | 3503 | 9% | 0% | 45 |
| 3 | Logic | 100 | 1% | 0% | 5 |
| 4 | Humanities, Multidisciplinary | 86 | 2% | 0% | 8 |
| 5 | Ethics | 57 | 1% | 0% | 6 |
| 6 | Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence | 53 | 3% | 0% | 16 |
| 7 | Linguistics | 32 | 1% | 0% | 7 |
| 8 | Language & Linguistics | 17 | 1% | 0% | 5 |
| 9 | Psychology, Experimental | 7 | 1% | 0% | 6 |
| 10 | Medieval & Renaissance Studies | 4 | 0% | 0% | 1 |
Address terms |
| Rank | Term | Chi square | Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
#P with term in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CNRS ETUD COGNIT | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 2 | EHESSENSCNRS | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 3 | GRUP RECERCA LOG LLENGUATGE COGNICIO | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 4 | LANGUAGE MET HYS | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 5 | PHILOS ANTHR STUDIES | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 6 | PHILOS UMIACS | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 7 | PHILOSOPH ANTROPOL STUDIES | 64284 | 0% | 100% | 1 |
| 8 | LOGIC MET HYSICS | 48208 | 1% | 25% | 3 |
| 9 | AHRC PHILOSOPHY LOG LANGUAGE MATH MIND | 41321 | 1% | 21% | 3 |
| 10 | AHRB PHILOSOPHY LOG LANGUAGE MATH MIND | 32141 | 0% | 50% | 1 |
Journals |
| Rank | Term | Chi square | Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
#P with term in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ANALYSIS | 113851 | 12% | 3% | 56 |
| 2 | MIND | 87168 | 8% | 4% | 36 |
| 3 | NOUS | 47024 | 7% | 2% | 32 |
| 4 | PHILOSOPHY AND PHENOMENOLOGICAL RESEARCH | 25436 | 5% | 2% | 26 |
| 5 | SYNTHESE | 23174 | 8% | 1% | 36 |
| 6 | PHILOSOPHICAL STUDIES | 19912 | 7% | 1% | 31 |
| 7 | AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHY | 14649 | 3% | 1% | 16 |
| 8 | JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHICAL LOGIC | 12086 | 3% | 1% | 13 |
| 9 | SOUTHERN JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHY | 10034 | 3% | 1% | 13 |
| 10 | PACIFIC PHILOSOPHICAL QUARTERLY | 9476 | 2% | 1% | 11 |
Author Key Words |
| Rank | Term | Chi square | Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
#P with term in class |
LCSH search | Wikipedia search |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VAGUENESS | 709403 | 11% | 21% | 52 | Search VAGUENESS | Search VAGUENESS |
| 2 | EPISTEMICISM | 393737 | 1% | 88% | 7 | Search EPISTEMICISM | Search EPISTEMICISM |
| 3 | SORITES PARADOX | 353551 | 2% | 50% | 11 | Search SORITES+PARADOX | Search SORITES+PARADOX |
| 4 | COXS THEOREM | 257136 | 1% | 100% | 4 | Search COXS+THEOREM | Search COXS+THEOREM |
| 5 | HIGHER ORDER VAGUENESS | 231417 | 1% | 60% | 6 | Search HIGHER+ORDER+VAGUENESS | Search HIGHER+ORDER+VAGUENESS |
| 6 | SORITES | 196862 | 1% | 44% | 7 | Search SORITES | Search SORITES |
| 7 | BORDERLINE CASES | 185281 | 1% | 41% | 7 | Search BORDERLINE+CASES | Search BORDERLINE+CASES |
| 8 | MARGIN FOR ERROR | 144637 | 1% | 75% | 3 | Search MARGIN+FOR+ERROR | Search MARGIN+FOR+ERROR |
| 9 | ONTIC VAGUENESS | 144637 | 1% | 75% | 3 | Search ONTIC+VAGUENESS | Search ONTIC+VAGUENESS |
| 10 | ALDINE EDITION OF GALEN 1525 | 128568 | 0% | 100% | 2 | Search ALDINE+EDITION+OF+GALEN+1525 | Search ALDINE+EDITION+OF+GALEN+1525 |
Core articles |
The table includes core articles in the class. The following variables is taken into account for the relevance score of an article in a cluster c: (1) Number of references referring to publications in the class. (2) Share of total number of active references referring to publications in the class. (3) Age of the article. New articles get higher score than old articles. (4) Citation rate, normalized to year. |
| Rank | Reference | # ref. in cl. |
Shr. of ref. in cl. |
Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BOBZIEN, S , (2010) HIGHER-ORDER VAGUENESS, RADICAL UNCLARITY, AND ABSOLUTE AGNOSTICISM.PHILOSOPHERS IMPRINT. VOL. 10. ISSUE 10. P. - | 21 | 100% | 1 |
| 2 | ZARDINI, E , (2013) HIGHER-ORDER SORITES PARADOX.JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHICAL LOGIC. VOL. 42. ISSUE 1. P. 25-48 | 16 | 94% | 1 |
| 3 | MONTMINY, M , (2016) A CONTEXTUALIST APPROACH TO HIGHER-ORDER VAGUENESS.SOUTHERN JOURNAL OF PHILOSOPHY. VOL. 54. ISSUE 3. P. 372 -392 | 13 | 100% | 0 |
| 4 | EKLUND, M , (2011) RECENT WORK ON VAGUENESS.ANALYSIS. VOL. 71. ISSUE 2. P. 352-363 | 12 | 100% | 2 |
| 5 | AKIBA, K , (2014) A DEFENSE OF INDETERMINATE DISTINCTNESS.SYNTHESE. VOL. 191. ISSUE 15. P. 3557 -3573 | 11 | 100% | 0 |
| 6 | AKIBA, K , (2004) VAGUENESS IN THE WORLD.NOUS. VOL. 38. ISSUE 3. P. 407-429 | 15 | 88% | 12 |
| 7 | AKERMAN, J , (2013) FORCED-MARCH SORITES ARGUMENTS AND LINGUISTIC COMPETENCE.DIALECTICA. VOL. 67. ISSUE 4. P. 403-426 | 11 | 92% | 0 |
| 8 | VARZI, AC , (2007) SUPERVALUATIONISM AND ITS LOGICS.MIND. VOL. 116. ISSUE 463. P. 633-675 | 13 | 76% | 18 |
| 9 | COBREROS, P , (2011) PARACONSISTENT VAGUENESS: A POSITIVE ARGUMENT.SYNTHESE. VOL. 183. ISSUE 2. P. 211-227 | 9 | 100% | 3 |
| 10 | LEE, CR , (2016) EXCLUDED KNOWLEDGE.SYNTHESE. VOL. 193. ISSUE 8. P. 2427 -2452 | 8 | 100% | 0 |
Classes with closest relation at Level 1 |